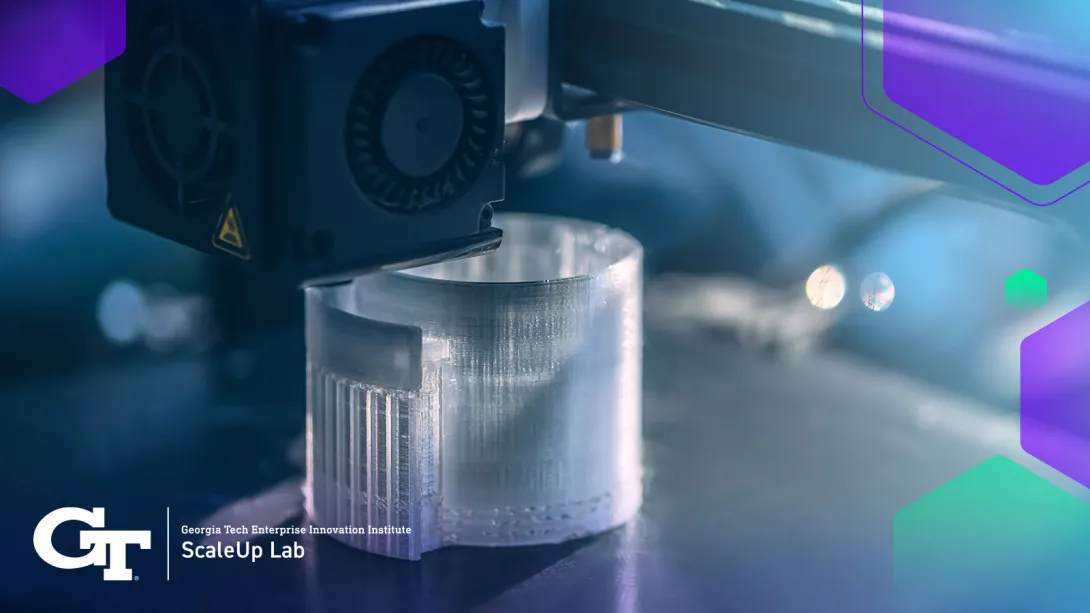
In recent years, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a groundbreaking technology with far-reaching implications across various industries. Initially used for rapid prototyping, 3D printing has evolved into a versatile tool for customized production and even construction. This comprehensive overview delves into the latest advancements in 3D printing technologies and their transformative potential in these domains.
1. Rapid Prototyping
1.1. Evolution of Rapid Prototyping
Traditionally, prototyping involved time-consuming processes such as CNC machining or injection molding, which were costly and limited in flexibility. However, with the advent of 3D printing, prototyping has undergone a paradigm shift. Additive manufacturing allows for the rapid creation of prototypes directly from digital designs, enabling iterative development and accelerating the product development cycle.
1.2. Materials and Precision
Advancements in 3D printing materials have expanded the range of prototypes that can be produced. From plastics and metals to ceramics and composites, the availability of diverse materials enables prototyping for various applications. Moreover, improvements in printing precision have enhanced the fidelity of prototypes, making them increasingly indistinguishable from final products.
1.3. Applications and Industries
The impact of rapid prototyping extends across industries, from automotive and aerospace to healthcare and consumer goods. Companies leverage 3D printing to iterate designs rapidly, test functionality, and gather feedback from stakeholders. This agility not only reduces time-to-market but also fosters innovation by enabling experimentation with novel concepts.
2. Customized Production
2.1. Personalized Products
One of the most significant advancements in 3D printing is its capacity for customized production. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which rely on mass production of standardized goods, additive manufacturing enables the creation of personalized products tailored to individual preferences and requirements. This customization ranges from consumer goods and fashion accessories to medical devices and prosthetics.
2.2. Mass Customization
The concept of mass customization, once deemed economically unfeasible, is now achievable through 3D printing. By leveraging digital design files and automated production processes, manufacturers can efficiently produce customized goods at scale. This hybrid approach combines the efficiency of mass production with the personalization of bespoke craftsmanship, offering consumers unparalleled choice and value.
2.3. Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Furthermore, 3D printing holds promise for sustainable manufacturing practices. By producing goods on-demand and minimizing material waste, additive manufacturing reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional mass production methods. Additionally, the ability to recycle and reuse printing materials contributes to a circular economy model, further mitigating environmental degradation.
3. Construction
3.1. Additive Construction Techniques
Beyond prototyping and customized production, 3D printing is revolutionizing the construction industry. Additive construction techniques, such as contour crafting and concrete printing, enable the fabrication of complex structures with unprecedented speed and efficiency. By depositing material layer by layer, 3D printers can construct buildings, bridges, and infrastructure with remarkable precision and minimal labor requirements.
3.2. Cost-effectiveness and Design Freedom
The adoption of 3D printing in construction promises cost-effectiveness and design freedom. Compared to traditional construction methods, which are labor-intensive and resource-intensive, additive manufacturing offers significant savings in time, labor, and material costs. Moreover, the flexibility of digital design enables architects and engineers to realize innovative and unconventional architectural forms that were previously impractical or unattainable.
3.3. Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the integration of robotics, automation, and advanced materials will further enhance the capabilities of 3D printing in construction. From on-site printing of affordable housing to the fabrication of intricate architectural facades, additive manufacturing is poised to redefine the built environment. Additionally, advancements in biodegradable and recyclable construction materials hold promise for sustainable urban development and resilient infrastructure.
Reflections and Future Directions
The advancements in 3D printing technologies have transformed prototyping, customized production, and construction, ushering in a new era of manufacturing innovation. As additive manufacturing continues to evolve, its impact will extend beyond industrial applications to reshape the way we design, produce, and interact with the world around us. However, challenges such as regulatory barriers, material limitations, and scalability constraints remain to be addressed. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and investing in research and development, we can unlock the full potential of 3D printing to address pressing societal needs and propel human progress in the 21st century.